Project scheduling is a critical aspect of project management that involves planning, organizing, and managing tasks and resources to ensure the project is completed on time. Below is a step-by-step explanation of how to create and manage a project schedule:
Step 1: Define Project Scope and Objectives
- Understand the project goals: Clearly define what the project aims to achieve.
- Identify deliverables: List all the outputs or outcomes the project will produce.
- Set boundaries: Determine what is included and excluded from the project scope.
Step 2: Break Down the Work (Work Breakdown Structure – WBS)
- Decompose the project: Divide the project into smaller, manageable tasks or work packages.
- Hierarchical structure: Organize tasks into levels (e.g., phases, deliverables, sub-tasks).
- Ensure completeness: Make sure all tasks are accounted for to avoid missing critical work.
Step 3: Define Task Dependencies
- Identify relationships: Determine the order in which tasks must be completed.
- Types of dependencies:
- Finish-to-Start (FS): Task B cannot start until Task A is finished.
- Start-to-Start (SS): Task B cannot start until Task A starts.
- Finish-to-Finish (FF): Task B cannot finish until Task A finishes.
- Start-to-Finish (SF): Task B cannot finish until Task A starts (rare).
- Use a network diagram: Visualize task dependencies to understand the flow of work.
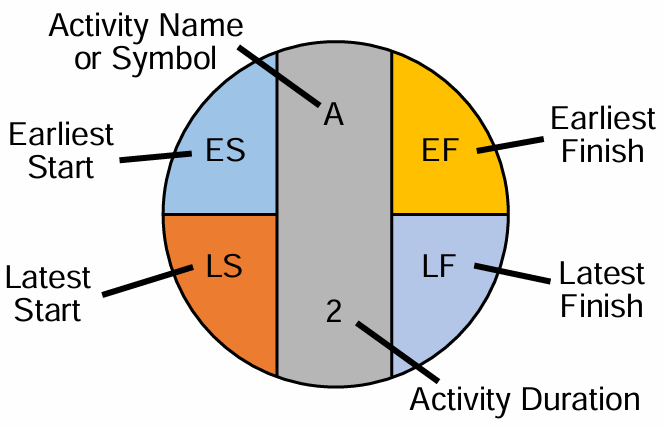
Step 4: Estimate Task Durations
- Gather input: Consult team members or experts to estimate how long each task will take.
- Consider resources: Account for the availability of resources (e.g., people, equipment).
- Use estimation techniques:
- Expert judgment: Rely on experienced team members.
- Analogous estimating: Use data from similar past projects.
- Parametric estimating: Use statistical relationships (e.g., cost per unit).
- Three-point estimating: Calculate optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely durations.
Step 5: Assign Resources
- Identify resources: Determine the people, equipment, and materials needed for each task.
- Allocate resources: Assign resources to tasks based on availability and skills.
- Avoid over-allocation: Ensure resources are not overburdened by too many tasks.
Step 6: Develop the Schedule
- Choose a scheduling tool: Use tools like Gantt charts, Microsoft Project, or software like Asana, Trello, or Jira.
- Input tasks, durations, and dependencies: Populate the tool with the information gathered.
- Set milestones: Identify key points in the project timeline (e.g., project phases, deliverables).
- Calculate critical path: Identify the longest sequence of dependent tasks that determine the project duration.
Step 7: Review and Optimize the Schedule
- Check for feasibility: Ensure the schedule is realistic and achievable.
- Identify bottlenecks: Look for tasks that could delay the project.
- Optimize resource allocation: Adjust resources to balance workloads.
- Consider buffers: Add contingency time for high-risk tasks.
Step 8: Baseline the Schedule
- Finalize the schedule: Once approved, set the schedule as the baseline.
- Document assumptions: Record any assumptions made during scheduling.
- Communicate the schedule: Share the baseline schedule with stakeholders and team members.
Step 9: Monitor and Control the Schedule
- Track progress: Regularly compare actual progress to the baseline schedule.
- Update the schedule: Adjust the schedule as needed to reflect changes or delays.
- Manage changes: Use a change control process to handle scope or schedule changes.
- Communicate updates: Keep stakeholders informed of any changes to the schedule.
Step 10: Close the Project
- Review the schedule: Analyze how well the schedule was followed and identify lessons learned.
- Document variances: Record any deviations from the baseline schedule.
- Archive the schedule: Store the final schedule for future reference.
Key Tools and Techniques for Project Scheduling
- Gantt Charts: Visual representation of tasks and timelines.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the longest path of dependent tasks.
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT): Uses probabilistic time estimates.
- Kanban Boards: Visual workflow management tool.
- Resource Leveling: Balances resource allocation to avoid overloading.
