Project Crashing is a project management technique used to shorten the project duration by adding additional resources to critical path tasks. It is typically employed when a project is behind schedule or when there is a need to meet an earlier deadline. However, crashing often comes at an increased cost, as it involves allocating more resources (e.g., labor, equipment, or materials) to complete tasks faster.
Key Concepts of Project Crashing
- Critical Path:
- The longest sequence of tasks in a project that determines the minimum project duration.
- Crashing focuses on tasks on the critical path because shortening non-critical tasks won’t reduce the overall project duration.
- Crash Time:
- The shortest possible time in which a task can be completed by adding additional resources.
- Crash Cost:
- The additional cost incurred to reduce the task duration to the crash time.
- Normal Time and Normal Cost:
- The original estimated time and cost to complete a task without additional resources.
Steps to Perform Project Crashing
- Identify the Critical Path:
- Determine the critical path and the tasks that are driving the project duration.
- Determine Crashable Tasks:
- Identify tasks on the critical path that can be shortened by adding resources.
- Calculate Crash Cost per Unit Time:
- For each task, calculate the cost of reducing its duration by one unit of time (e.g., per day or week).
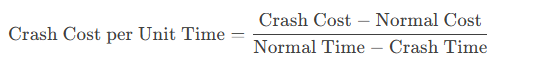
- Choose the Most Cost-Effective Tasks:
- Prioritize tasks with the lowest crash cost per unit time to minimize additional costs.
- Apply Resources and Adjust the Schedule:
- Allocate additional resources to the selected tasks and update the project schedule.
- Monitor the Impact:
- Track the changes in the project timeline and budget to ensure the crashing is effective.
Example of Project Crashing
Suppose a project has the following tasks on the critical path:
| Task | Normal Time (Days) | Crash Time (Days) | Normal Cost ($) | Crash Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 5 | 3 | 500 | 800 |
| B | 7 | 5 | 1000 | 1400 |
| C | 4 | 2 | 600 | 1000 |
- Calculate Crash Cost per Day:
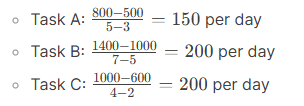
2. Choose the Most Cost-Effective Task:
- Task A has the lowest crash cost per day ($150).
3. Crash Task A:
- Reduce Task A from 5 days to 3 days.
- Additional cost: 2×150=3002×150=300.
4. Update Project Duration:
- The project duration is reduced by 2 days.
Advantages of Project Crashing
- Helps meet tight deadlines.
- Improves flexibility in project scheduling.
- Can prevent penalties for late delivery.
Disadvantages of Project Crashing
- Increases project costs due to additional resources.
- May lead to reduced quality if tasks are rushed.
- Not all tasks can be crashed (e.g., tasks with fixed durations).
When to Use Project Crashing
- When the project is behind schedule.
- When there is a fixed deadline that must be met.
- When the benefits of completing the project earlier outweigh the additional costs.
By carefully analyzing the trade-offs between time and cost, project managers can use crashing to effectively manage project timelines while minimizing negative impacts.
