Que-1:: A Magento Open Source merchant sell toys and gift and wants to improve the experience on their website. The merchant wants to avoid extensions or customization.
Continue reading “AD0-E708 Adobe Certified Expert Magento Commerce Business Practitioner”Month: June 2022
Why Need To Use SOLID Principles in Programming?
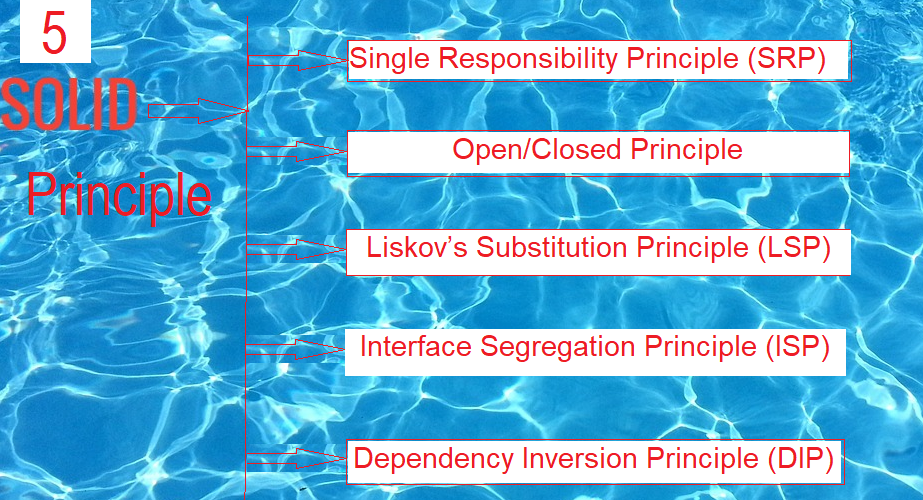
SOLID Principles are coding standard that all developers / programmers must have follow as good understanding rules / regulations to develop software properly.
SOLID is an acronym that stands for five key design principles:
S – stands for Single-Responsibility Principle
O – stands for Open-Closed Principle
L – stands for Liskov Substitution Principle
I – stands for Interface Segregation Principle
D – stands for Dependency Inversion Principle
Single Responsibility Principle [SRP] :: very class should have a single responsibility or single job or single purpose and only one reason to change, meaning that a class should have only one job.
For Example Single Responsibility Principle:: While developing software, The task is divided into different members doing different things as
- Front-end designers do design
- Tester does testing
- Backend developer takes care of backend development
- Mobile App developer takes care of mobiles app development
Finally, we can say that everyone has a single job or responsibility.
Liskov’s Substitution Principle:: “Derived or child or sub classes must be substitutable for their base or parent classes“. This principle ensures that any class that is the child of a parent class should be usable in place of its parent without any unexpected behavior.
For Example Liskov’s Substitution Principle:: One of the classic examples of this principle is a rectangle having four sides. A rectangle’s height can be any value and width can be any value. A square is a rectangle with equal width and height. So we can say that we can extend the properties of the rectangle class into square class.
Interface Segregation Principle [ISP]:: A system / client should never be forced to implement an interface that it doesn’t use, or clients shouldn’t be forced to depend on methods they do not use.
For Example Interface Segregation Principle:: Suppose if you enter a restaurant and you are pure vegetarian. The waiter in that restaurant gave you the menu card which includes vegetarian items, non-vegetarian items, drinks, and sweets. In this case, as a customer, you should have a menu card which includes only vegetarian items, not everything which you don’t eat in your food. Here the menu should be different for different types of customers. The common or general menu card for everyone can be divided into multiple cards instead of just one. Using this principle helps in reducing the side effects and frequency of required changes..
SOLID principle was introduced by Robert C. Martin, also known as Uncle Bob and it is a coding standard in programming.
GraphQL Interview Questions & Answers
Que-1:: What is GraphQL?
Ans-1:: GraphQL is a query language & used for APIs and includes the runtime for executing these queries.
Que-2:: When development of GraphQL has been started??
Ans-2:: GraphQL was developed internally by Facebook in 2012 and publicly released in 2015. The complete Facebook moved into GraphQL on 7 November 2018 as newly established GraphQL Foundation, hosted by the non-profit Linux Foundation.
Que-3:: Mention list of companies using GraphQL?
Ans-3:: There are following below companies using GraphQL
Facebook, Shopify, and Instagram, Twitter, Stack, Stackshare,
Microsoft, Coursera, KAVAK, Graphy, Klarna & many more as below
Que-4:: GraphQL is a Database?
Ans-4:: GraphQL is not DBMS / RDBMS, It is a Query Language used for APIs.
Que-5:: List of languages those are used to implement GraphQL Server.?
Ans-5:: The following below languages used to implement GraphQL.
JavaScript, Python, Java, PHP, Haskell, Ruby, C#, Scala, Go, Elixir, Erlang, R, and Clojure etc.
Que-6:: What is response format of GraphQL?
Ans-6:: GraphQL response as JSON format.
Que-7:: Define Overfetching in GraphQL?
Ans-7:: Overfetching is used to fetch extra data for an API request. Overfetching increases payload size..
Que-8:: Define underfetching in GraphQLL?
Ans-8:: Underfetching is used to fetch enough data. Underfetching requires multiple API calls to fetch the complete data..
Que-9:: How GraphQL helping in data loading process?
Ans-9:: GraphQL always allow the minimum number of data that is exactly required by the client, in case of the object model having a lot of fields, the client request only the required fields..
Adobe AD0-E700 Exam Has Been Replaced By AD0-E708 Exam
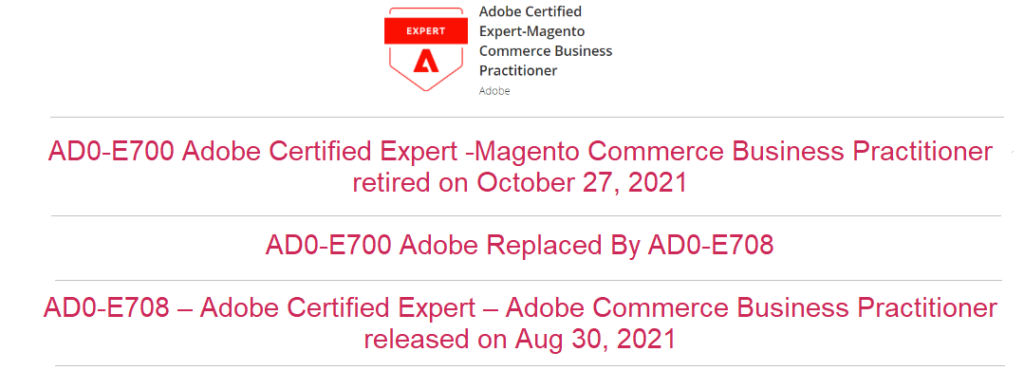

AD0-E708 Adobe Commerce Business Practitioner Expert exam is the new exam replacement of AD0-E700 Adobe Certified Expert -Magento Commerce Business Practitioner which has been retired
October 27, 2021
AD0-E708 – Adobe Certified Expert – Adobe Commerce Business Practitioner released on Aug 30, 2021
AD0-E708 Adobe Certified Expert -Magento Commerce Business Practitioner is an expert user of the Magento 2.x Commerce platform. Drawing on a deep background in business and ecommerce, the Adobe Certified Expert Magento Commerce Business Practitioner can efficiently align business objectives with Magento 2 functionality, optimize use of native features, and avoid unnecessary customization. Whether as a merchant, a manager, a consultant, or an analyst, the Adobe Certified Expert – Adobe Commerce Business Practitioner knows how to make the best use of Magento 2.x technology
- Adobe AD0-E708 Exam Information
- Exam number- AD0-E708
- Exam name- Adobe Certified Expert – Adobe Commerce Business Practitioner
- Certificate level- Certified Expert
- Status- Active
- Available languages- English
- Number of questions- 50
- Formats- Multiple choice
- Duration- 120 minutes
- Delivery- Onsite/Online proctored (requires camera access) or test center proctored
- Passing mark- 30/50
- Price- $225 USD / $150 USD (India only)
Adobe AD0-E708 Adobe Certified Expert – Adobe Commerce Business Practitioner Syllabus :: described following below various Syllabus part
Part 1- Core Features / General Configuration ::
- Identify the features of Adobe Commerce Open Source Edition and Commerce Edition
- Distinguish the differences between all editions of Adobe Commerce products
- Determine how to utilize product types and their features to meet customer requirements
- Interpret requirements and mock ups to determine if they can be met with native functionality
- Demonstrate knowledge of the admin panel and the location of common features
- Demonstrate the ability import/export Adobe Commerce entities
- Understand how to natively configure cart and checkout
- Evaluate the native available shipping methods in Adobe Commerce and how they apply to common use cases
- Understanding the ways to create and publish stylized content using the Adobe Commerce CMS features including Page Builder
- Using native tools to manage the order life cycle
- Demonstrate the ability to configure the various gifting options (gift cards, gift wrapping, give messages)
- Configuring and modifying transactional emails
- Explain the customer self service and loyalty program native features in B2B
Part 2- Merchandising ::
- Demonstrate the ability to create promotions to meet specific business criteria and how it determines final pricing
- Demonstrate ability to manage categories and products
- Understanding the different pricing configurations and how they affect the final price
Par 3- Digital Marketing ::
- Recommend best practices for SEO using native features
- Assess common metrics in Google Analytics and BI
Par 4- Add-on Modules and additional products ::
- Describe the B2B functionality and how it relates to common B2B scenarios
- Apply business requirements to suggest a solution using MSI
- Explain the advantages and how to use BI to the Adobe Commerce solution
- Distinguish the differences between native search and Live Search
- Apply business requirements to determine how to apply taxes, duties and exemptions in a B2B environment
- Understand how to apply tailored pricing to a B2B customer
- Understand the differences between Adobe Commerce native product and Adobe Sensei product recommendations
Part 5- Systems Architecture ::
- Evaluate requirements to determine which websites, stores, and store view are necessary
- Identify and analyze performance metrics to make improvements
- Understand the available methods to integrate external system with Adobe Commerce
- Differentiate between headless approaches and traditional
Part 6- Compliance / Security ::
- Demonstrate how to secure the Adobe Commerce data access with roles and permissions
- Understand basics of compliance for privacy laws and payment security
- Explain common security aspects of an Adobe Commerce project
- Understand the basics of tax laws and how to configure
List of All Adobe Commerce / Magento 2 Certification