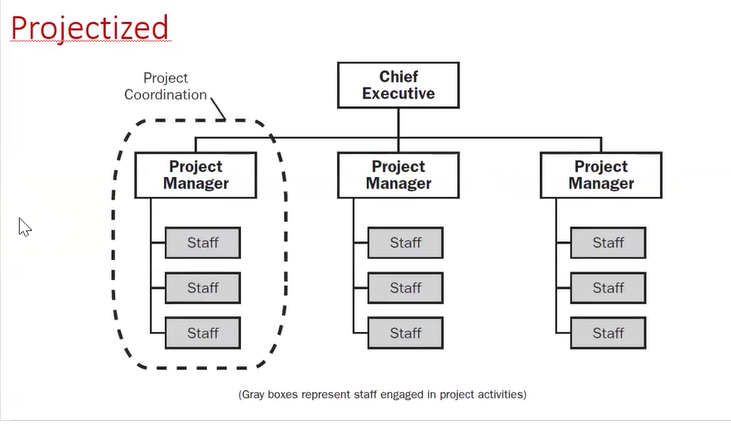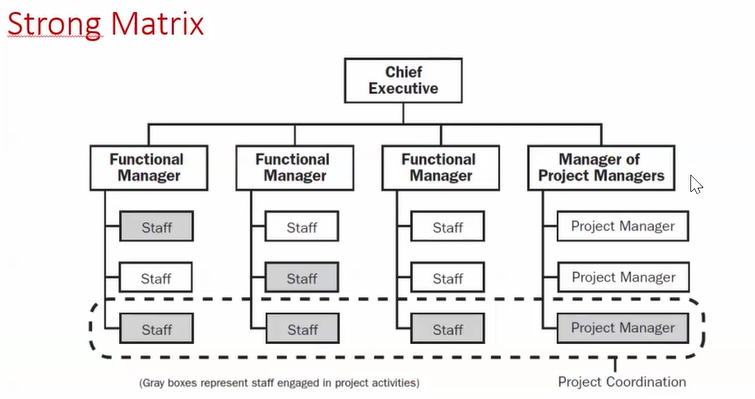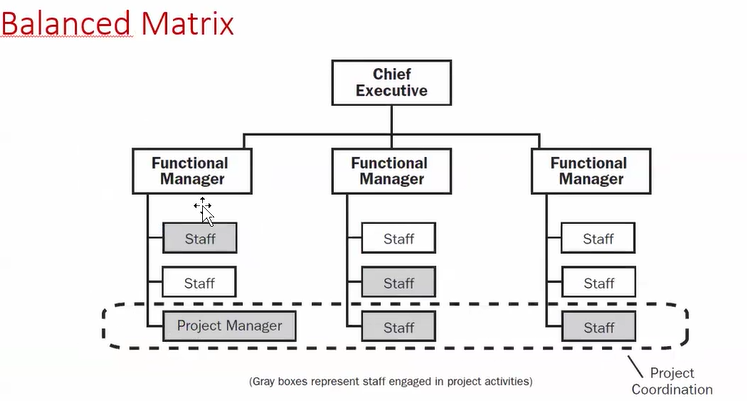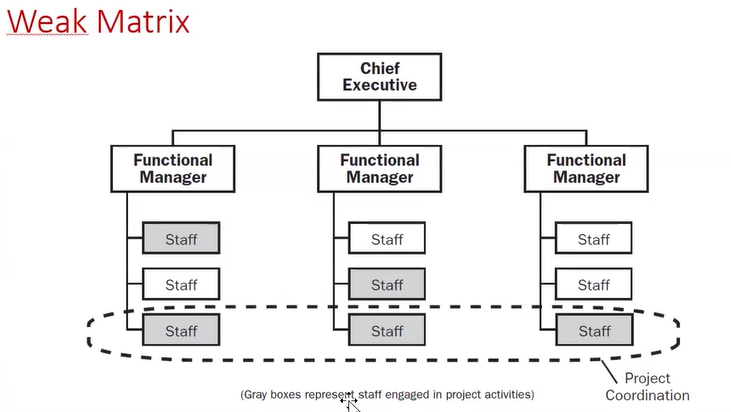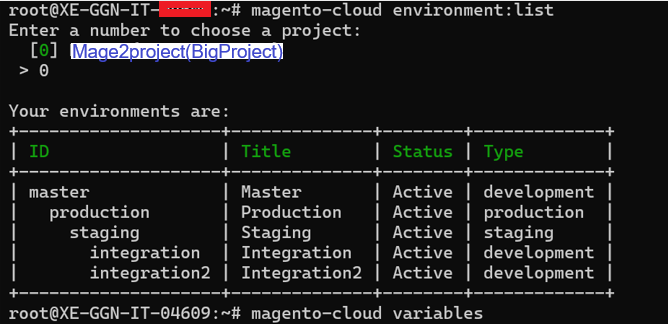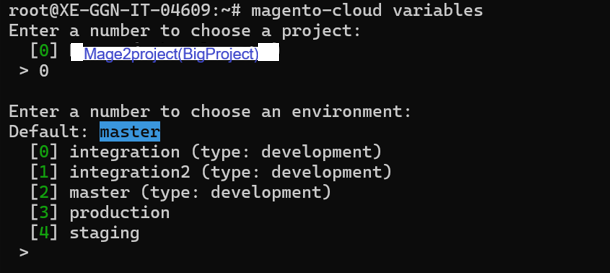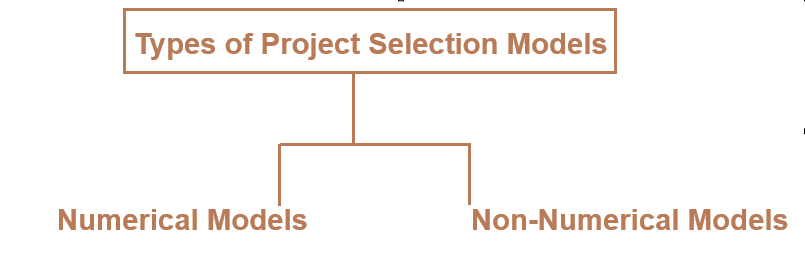


There are two basic types of project selection models, numeric and non-numeric. Both are widely used. Many organization use both at the same time or they use models that are combinations of the two
1. Numerical Models
Numerical models are quantitative methods that use numerical data and calculations to evaluate and compare projects.
Characteristics:
- Relies on measurable data (e.g., costs, revenues, time).
- Objective and data-driven.
- Focuses on financial or quantifiable outcomes.
Types of Numerical Models:
- Profitability Models:
- Evaluate financial viability.
- Examples:
- Net Present Value (NPV): Measures the present value of cash flows against investment costs.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): Calculates the discount rate where NPV equals zero.
- Payback Period: Time required to recover the project investment.
- Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR): Ratio of benefits to costs; a higher BCR is preferred.
- Scoring Models:
- Assigns weights to criteria based on importance and scores projects accordingly.
- Example:
- Weighted Scoring Model: Combines scores across criteria (e.g., risk, ROI, alignment with strategy).
Advantages:
- Provides clear, comparable metrics.
- Helps assess financial feasibility and return on investment.
Disadvantages:
- May overlook non-quantifiable benefits (e.g., reputation, employee satisfaction).
2. Non-Numerical Models
Non-numerical models are qualitative approaches that rely on subjective assessments and strategic considerations.
Characteristics:
- Focuses on alignment with organizational goals and priorities.
- Emphasizes qualitative factors like innovation, market trends, or social impact.
- Less dependent on numerical data.
Types of Non-Numerical Models:
- Checklist Model:
- Projects are evaluated using a checklist of criteria (e.g., “Does it align with organizational goals?”).
- Simple “yes” or “no” answers determine project viability.
- Strategic Alignment Model:
- Assesses how well a project aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Profile Model:
- Compares projects based on risk and return profiles.
- Helps visualize trade-offs between risk and potential benefits.
- Sacred Cow Model:
- Projects are selected based on leadership preferences or strategic directives, regardless of other factors.
Advantages:
- Captures non-financial and strategic benefits.
- Useful for innovative or exploratory projects.
Disadvantages:
- Subjective and prone to bias.
- Lacks consistency across evaluations