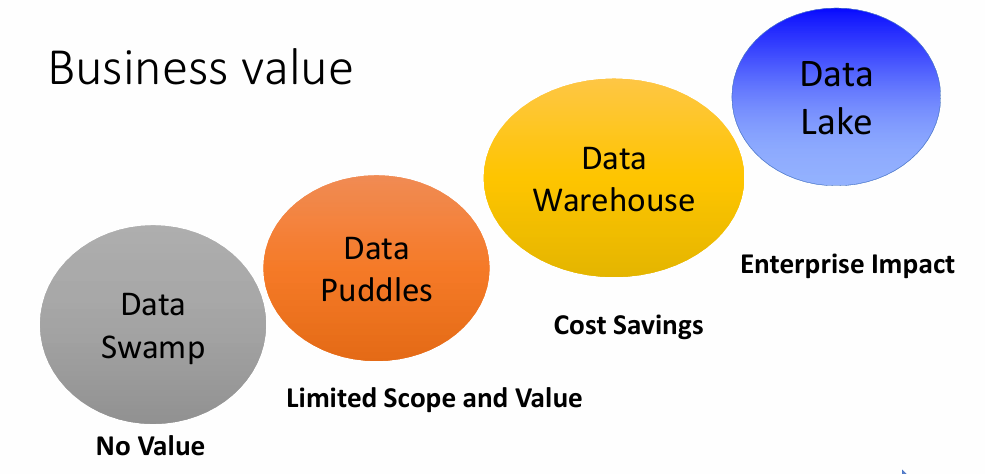
1. Data Swap (Data Mart)
A Temporary storage location where data is exchanged or transferred between two systems, It typically handles small transactional data in a structured format.
- Definition: A small, focused subset of a data warehouse designed for a specific department or team.
- Scope: Limited to a single business unit (e.g., Sales, Marketing).
- Purpose: Quick access to relevant data for specific needs.
- Structure: Highly structured and pre-processed.
- Example:
- A sales data mart containing monthly sales, customer data, and product performance for the sales department.
- I a E-commerce, when a customer makes a payment , the payment gateway system exchanges transaction details with the Order Mgt System.
2. Data Puddles
Small, isolated collections or data typically focused on a specific department or project. These are often uncoordinated & may no follow a consistent schema.
- Definition: A small-scale, isolated data repository created by individual teams for short-term use.
- Scope: Project or Department specific or team-specific with minimal governance.
- Purpose: Temporary storage for ad-hoc analysis or experiments.
- Structure: Semi-structured or unstructured, often created for quick insights.
- Example:
- A marketing team’s Excel sheets and Google Drive files collecting social media metrics for a campaign.
- It serves marketing specific needs but is not accessible across other departments.
3. Data Warehouse
A centralized repository of structured data that is cleaned, organized & optimized for querying & reporting.
Data Warehouses support Business Intelligence(BI) & analytics by integrating data from multiple sources.
- Definition: A centralized, structured repository that stores processed and organized data from multiple sources.
- Scope: Enterprise-wide, integrating data from across the organization.
- Purpose: Supports business intelligence (BI), reporting, and analysis.
- Structure: Highly structured with defined schemas (star/snowflake schemas).
- Example:
- Amazon Redshift or Google BigQuery storing customer transactions, inventory, and supply chain data for reporting and forecasting.
- An otg
4. Data Lake
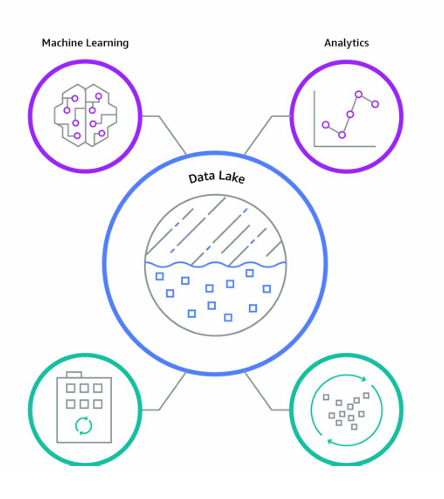
A scalable repository that stores vast amounts of data as
Structured Data Format, Unstructured Data Format, Semi Structured Data Format.
It is used for advanced analytics, machine learning & big data
- Definition: A vast, unstructured repository that stores raw data from various sources in its native format.
- Scope: Enterprise-wide with the ability to store massive datasets.
- Purpose: Enables advanced analytics, machine learning (ML), and data discovery.
- Structure: Unstructured or semi-structured; no predefined schema.
- Example:
- AWS S3 or Azure Data Lake storing IoT sensor data, social media feeds, and raw logs for future analysis.
- An organization uses data warehouse (Snowflake or Amazon redshift) to coordinate sales, customer & financial data, It allows analysts to create dashboards & generate reports for long term business strategy.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Data Swap (Mart) | Data Puddle | Data Warehouse | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Department-specific | Project or team-specific | Organization-wide | Organization-wide |
| Data Structure | Structured | Semi-structured/unstructured | Structured | Unstructured/semi-structured |
| Data Volume | Small to medium | Small | Large | Very large |
| Purpose | Specific business unit reporting | Temporary/quick analysis | Reporting & BI | Advanced analytics & big data |
| Storage Format | Pre-processed | Raw | Pre-processed | Raw |
| Processing | Minimal | Minimal | Extensive ETL | ELT (Extract, Load, Transform later) |
| Example | Sales Mart for KPIs | Excel files for project insights | Enterprise-wide BI reports | IoT sensor and video data repository |
