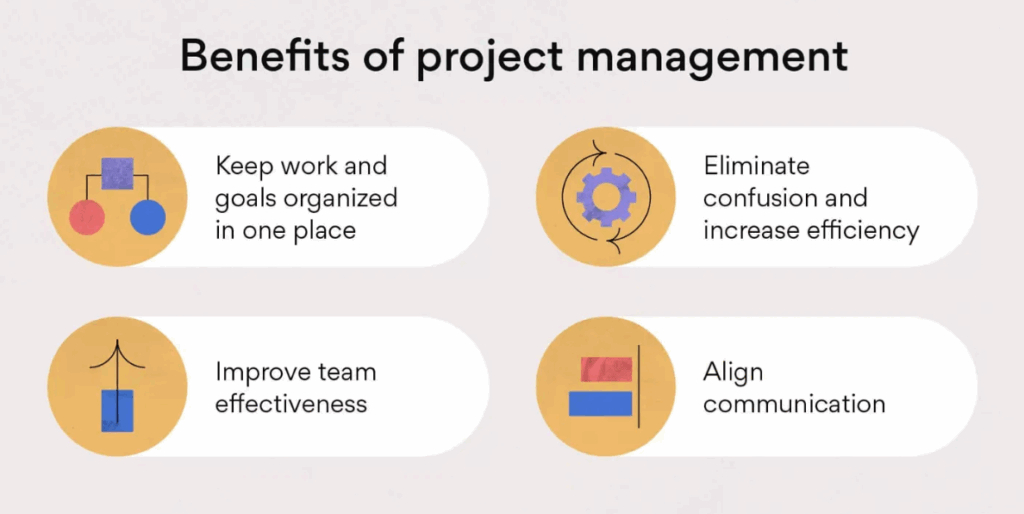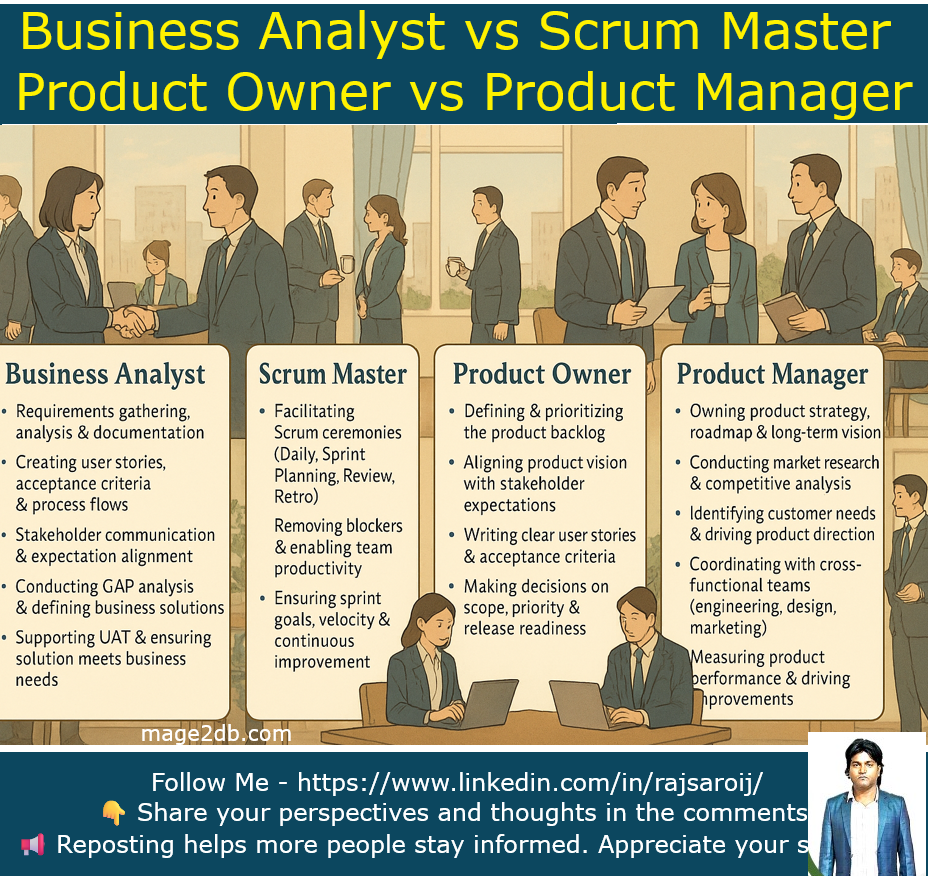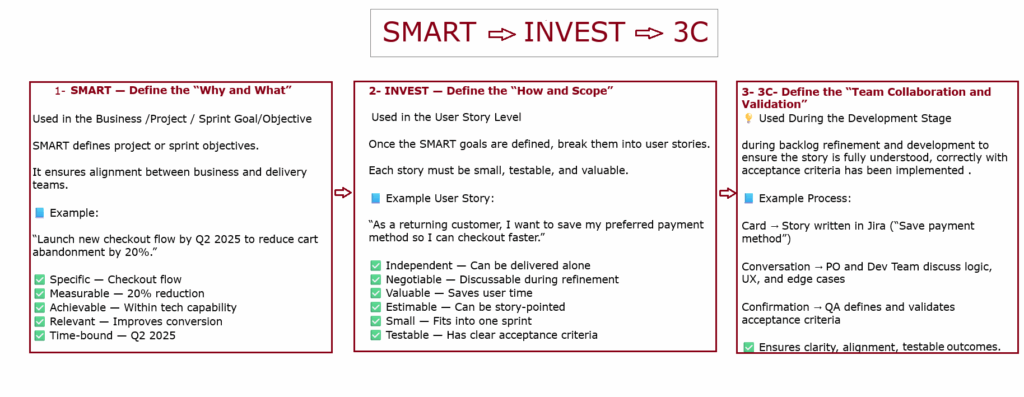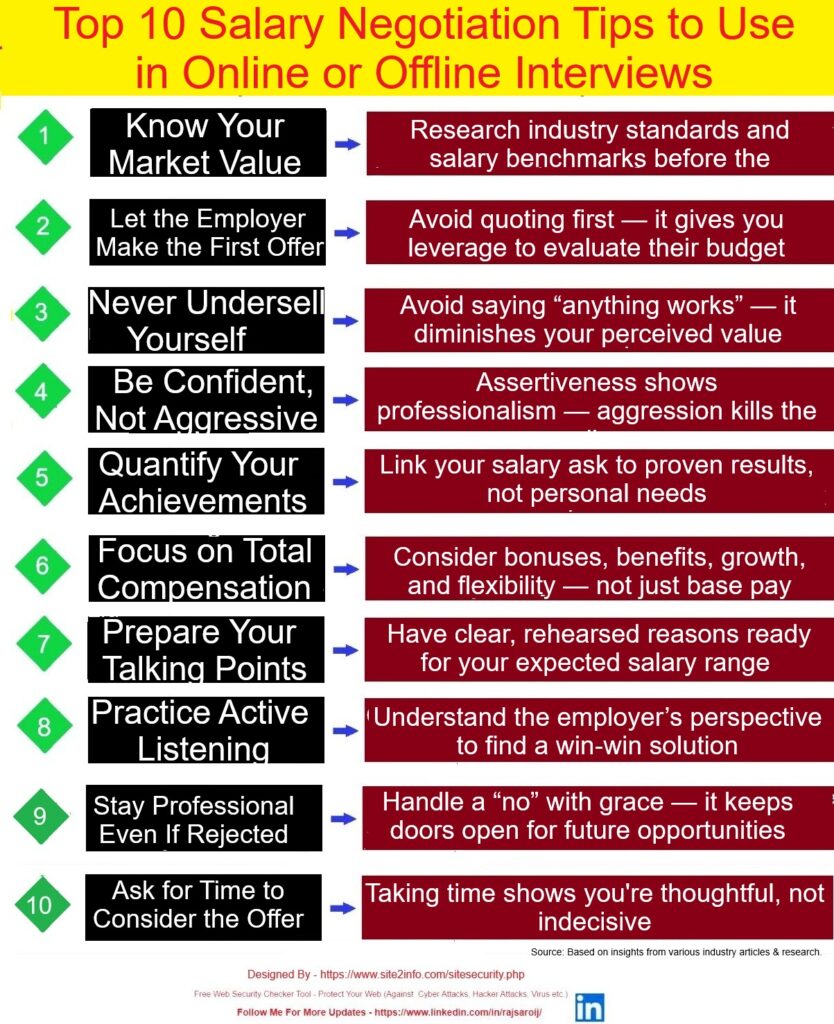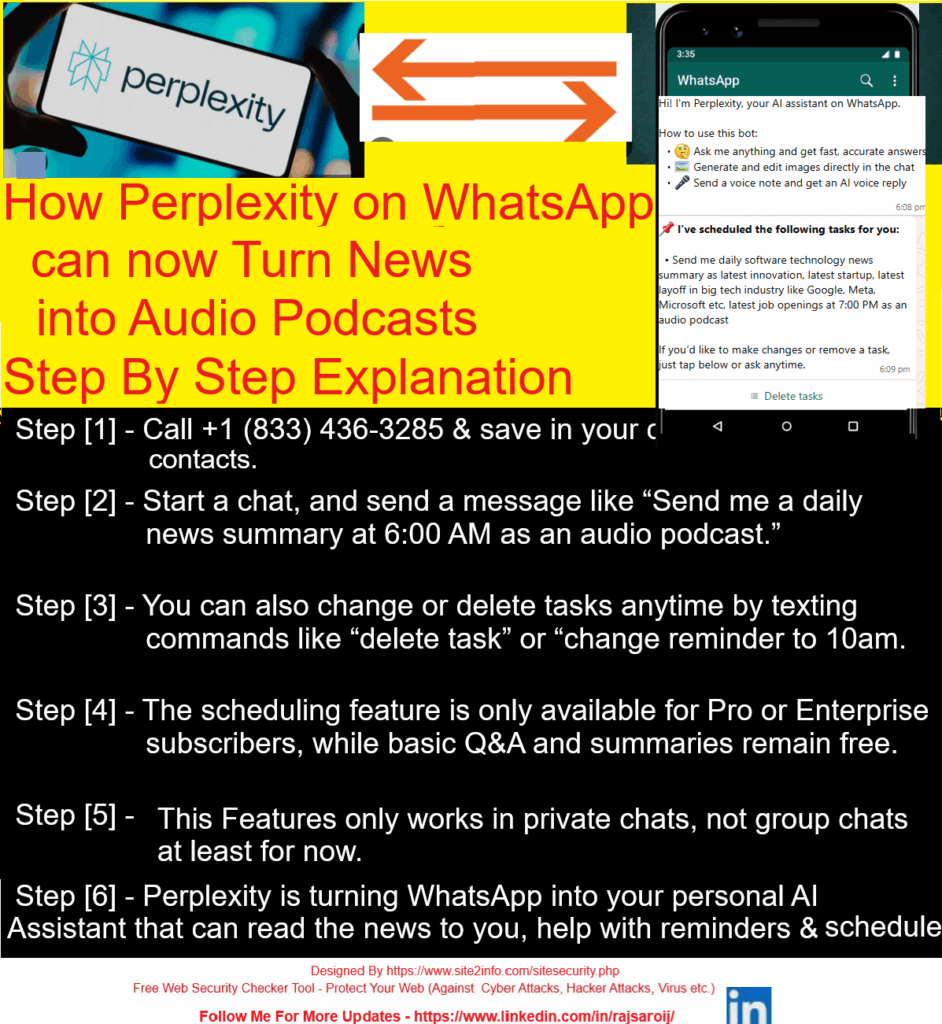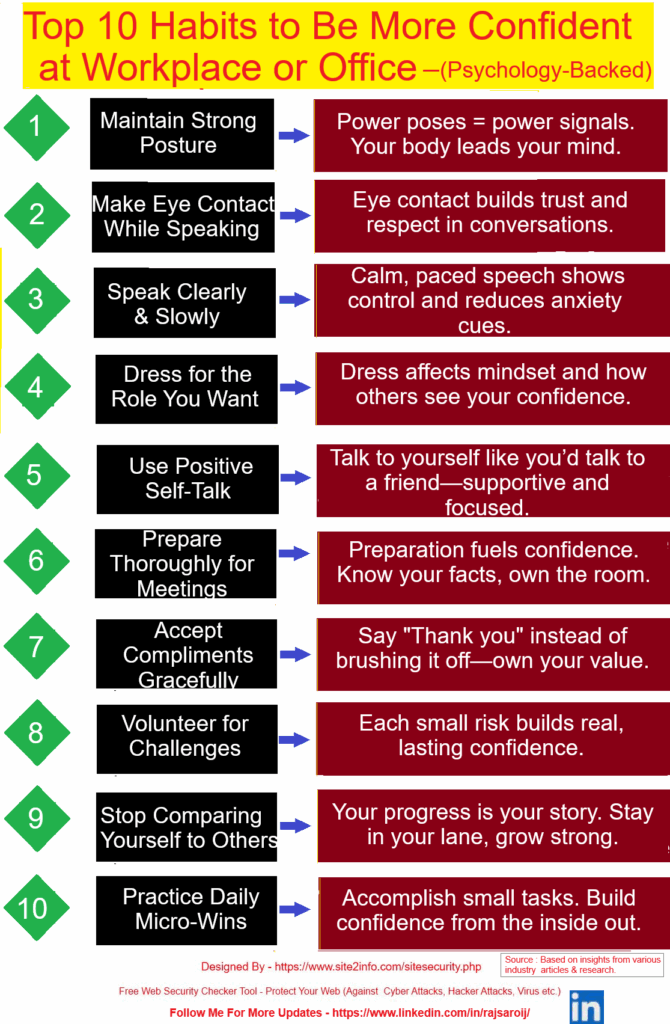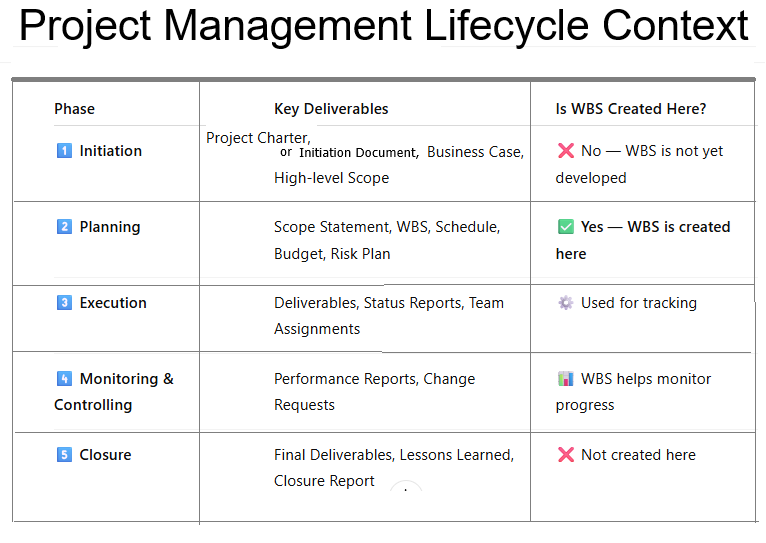
These are the 5 Project Management Process Groups defined by PMI (Project Management Institute) in the PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge).
These are NOT SDLC phases — they are Project Management Phases used in any type of project, including IT, software, construction, and business operations.
1️⃣ Initiation Phase
Purpose: Start the project formally
Activities include:
- Define project goals
- Create Project Charter
- Identify stakeholders
- High-level scope & feasibility
2️⃣ Planning Phase
Purpose: Plan how the project will be executed
Activities include:
- Detailed project plan
- Scope planning
- Schedule & timeline
- Budget planning
- Risk management plan
- Resource planning
- Communication plan
3️⃣ Execution Phase
Purpose: Do the actual work
Activities include:
- Team execution
- Development, design, testing
- Managing stakeholders
- Quality management
- Task assignments
- Delivering project outputs
4️⃣ Monitoring & Controlling Phase
Purpose: Track progress and control deviations
Activities include:
- Monitor KPIs
- Control scope changes
- Track timeline and budget
- Ensure quality standards
- Issue/risk management
- Status reporting
5️⃣ Closure Phase
Purpose: Formally end the project
Activities include:
- Final deliverables
- Approvals and sign-off
- Documentation
- Lessons learned
- Release resources
- Project completion report