
1. Product Scope
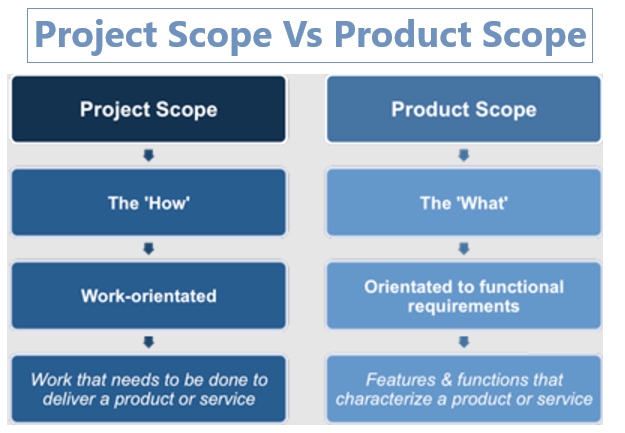
The product scope defines the features, functionalities, and characteristics of the final product or deliverable that the project is meant to create. It answers the “what” question: What does the product include?
Product Scope: Focuses on what the product will be (the end result)
Features of Product Scope:
- Focus: On the product itself.
- Defined By:
- Functional requirements (e.g., “The website must support online payments”).
- Non-functional requirements (e.g., “The app must load within 3 seconds”).
- Features, quality, and performance criteria.
- Validation: Measured by whether the product meets the specified requirements (e.g., user acceptance testing, feature testing).
Example of Product Scope
For an e-commerce website project:
- Product Scope Includes:
- A fully functional website with online payment capability.
- A product search feature.
- Integration with an inventory management system.
2. Project Scope
The project scope defines all the work required to deliver the product. It focuses on the “how” question: How will the product be delivered?
Project Scope: Focuses on how the product will be created (the process).
Features of Project Scope:
- Focus: On the work and processes involved in creating the product.
- Defined By:
- Activities, tasks, and deliverables needed to complete the project.
- Resource allocation, timelines, and constraints.
- Processes for risk management, quality assurance, and communication.
- Validation: Measured by whether the project achieves its objectives on time and within budget (e.g., project completion review).
Example of Project Scope
For the e-commerce website project:
- Project Scope Includes:
- Designing the website layout.
- Developing the payment integration.
- Testing the website functionality.
- Deploying the website on a server.
- Training staff to manage the website.
Combined Example of Project Scope & Product Scope

