1. What is Magento 2 and how does it differ from Magento 1?
- Answer: Magento 2 is the latest version of the Magento eCommerce platform, offering improved performance, scalability, and new features compared to Magento 1. Key differences include:
- Architecture: Magento 2 has a more modular codebase with a modern tech stack.
- Performance: Improved indexing, caching, and optimized checkout process.
- User Experience: Responsive design and better admin interface.
- Database: Supports multiple databases for different functions (e.g., checkout, orders, and product data).
- Extensions: Simplified integration with third-party extensions and APIs.
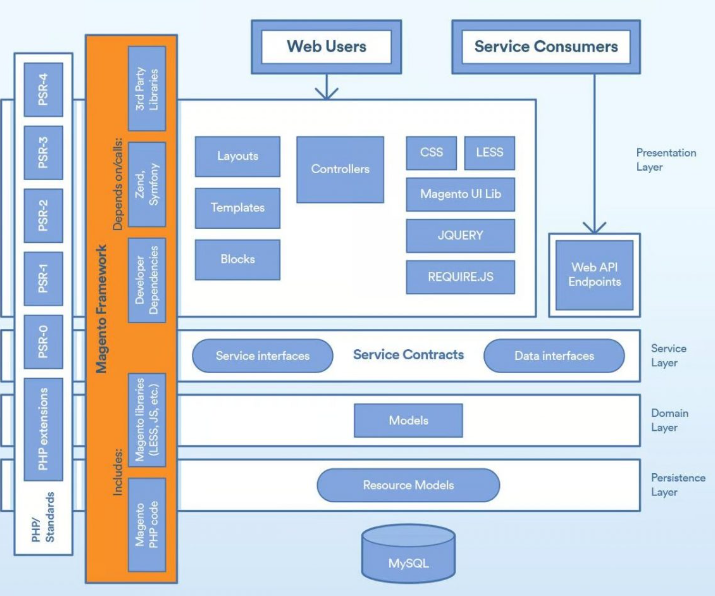
2. Can you explain the Magento 2 architecture?
- Answer: Magento 2 architecture is based on a modular system, separating code into individual modules. The architecture includes:
- Presentation Layer: Contains blocks, layouts, and templates.
- Service Layer: Provides a set of interfaces and service contracts.
- Domain Layer: Business logic, typically found in models.
- Data Layer: Database access, repository pattern, and entities.
- Integration Layer: APIs, web services, and external system integrations.
- Dependency Injection (DI): Magento 2 uses DI to manage class dependencies, improving testability and flexibility.
- Event-Observer and Plugins: Allows customization and extension of core functionalities.
3. What is Dependency Injection in Magento 2? How does it work?
- Answer: Dependency Injection (DI) is a design pattern used in Magento 2 to manage object dependencies. It allows objects to be passed to other objects through constructors or setters, rather than creating instances directly. This increases flexibility and makes the system more testable.
- How it works: Magento 2 uses an XML-based configuration to declare dependencies. The DI framework automatically injects the required dependencies when an object is instantiated.
4. How do you manage caching in Magento 2?
- Answer: Magento 2 uses several types of caching to improve performance, including:
- Configuration Cache: Caches system configuration.
- Page Cache: Caches full page content (supports Varnish).
- Block Cache: Caches individual blocks.
- Collection Cache: Caches database queries.
- Session Cache: Stores session data.
- Caches can be managed through the Magento Admin Panel under “System > Cache Management” or via the CLI using
bin/magento cache:enable/disable/clean/flushcommands.
5. Explain the concept of Service Contracts in Magento 2.
- Answer: Service Contracts are a set of PHP interfaces used to define the APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) of the business logic in Magento 2. They provide a stable API, ensuring backward compatibility and are designed to be used by modules, web services, or third-party developers.
- Key Components:
- Data Interfaces: Define the structure of the data (e.g.,
CustomerInterface,OrderInterface). - Service Interfaces: Define operations related to the business logic (e.g.,
CustomerRepositoryInterface,ProductRepositoryInterface).
- Data Interfaces: Define the structure of the data (e.g.,
- Key Components:
6. What is the purpose of Composer in Magento 2?
- Answer: Composer is a dependency manager used in Magento 2 to manage PHP libraries, modules, and dependencies. It helps in:
- Dependency Management: Automatically installs and updates packages and libraries that Magento or its modules depend on.
- Autoloading: Composer provides autoloading for classes, reducing the need to manually include files.
- Version Control: Manages version control of dependencies, ensuring compatibility between modules and core Magento functionality.
7. How do you approach customization in Magento 2?
- Answer: Customization in Magento 2 should follow best practices to ensure maintainability and upgradability:
- Using Plugins: Allows you to modify the behavior of public methods in a class without overriding the entire class.
- Observers: Listen to events and execute code when the event is triggered.
- Overrides: Use carefully to avoid conflicts, usually by creating custom modules rather than directly modifying core files.
- Layouts and Templates: Customizing the presentation layer using XML layout files and PHTML templates.
- Service Contracts: Prefer using service contracts for business logic changes to maintain a stable API.
8. What are Magento 2 modules and how do you create one?
- Answer: Magento 2 modules are the building blocks of a Magento application. They contain the code needed to add features or functionality. To create a module:
- 1. Create the module directory structure:
app/code/VendorName/ModuleName
- 2. Create the module’s
registration.phpfile to register the module with Magento. - 3. Create the
module.xmlfile inetcfolder to define module details. - 4. Configure
composer.jsonto manage dependencies. - 5. Define necessary configurations in
etc(e.g., routes, events, di.xml). - 6. Run
bin/magento setup:upgradeto install the module.
- 1. Create the module directory structure:
9. How do you manage security in a Magento 2 application?
- Answer: Security in Magento 2 can be managed through:
- Applying Patches: Regularly apply security patches provided by Magento.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for the admin panel.
- Secure Admin URLs: Change the default admin URL and limit access by IP.
- Use HTTPS: Enforce HTTPS for all frontend and backend operations.
- Role-Based Access Control: Create specific user roles and permissions to limit access to sensitive areas.
- Data Sanitization: Always sanitize user input and use Magento’s built-in methods to avoid SQL injection, XSS, and other attacks.
10. Explain the role of Magento 2 CLI.
- Answer: Magento 2 Command Line Interface (CLI) provides a set of commands to perform various tasks, including:
- Setup and Configuration:
bin/magento setup:install,bin/magento config:set. - Cache Management:
bin/magento cache:clean,bin/magento cache:flush. - Module Management:
bin/magento module:enable,bin/magento module:disable. - Index Management:
bin/magento indexer:reindex. - Deployment:
bin/magento setup:upgrade,bin/magento deploy:mode:set.
- Setup and Configuration:
11. What is Varnish and how is it used in Magento 2?
- Answer: Varnish is a web application accelerator (cache) used to improve website performance by caching content and serving it directly from memory. In Magento 2:
- Full Page Cache (FPC): Varnish can be used as the FPC, reducing the load on the web server and speeding up page delivery.
- Configuration: Varnish can be configured in Magento 2 under
Stores > Configuration > Advanced > System > Full Page Cache. - Integration: Magento 2 provides VCL (Varnish Configuration Language) files to integrate Varnish, which can be customized according to the environment.
12. How do you optimize performance in Magento 2?
- Answer: Optimizing performance in Magento 2 involves:
- Caching: Use Varnish for FPC, enable Redis for session and cache storage.
- Indexing: Set indexers to “Update on Schedule” for better performance.
- Optimization Tools: Use tools like Minify HTML/CSS/JS and merge CSS/JS files.
- CDN: Use a Content Delivery Network to deliver content faster to users.
- Database Optimization: Regularly clean logs, optimize database tables, and use proper indexes.
- Image Optimization: Compress images and use responsive images to reduce load time.
- Server Configuration: Ensure proper server resources (CPU, memory), PHP version (7.4+), and enable OPcache.
13. What is the Magento 2 Layout XML and how does it work?
- Answer: Layout XML in Magento 2 is used to define the structure and content of a page. It controls which blocks are displayed, in what order, and where.
- Key Elements:
<block>: Defines a block of content.<container>: Defines a container that can hold blocks.<referenceBlock>and<referenceContainer>: Modify existing blocks/containers.<remove>: Removes blocks or containers.
- Usage: Layout XML is defined in module or theme specific XML files, such as
default.xml,catalog_product_view.xml, etc.
- Key Elements:
14. How do you handle multi-store functionality in Magento 2?
- Answer: Magento 2’s multi-store functionality allows you to manage multiple websites, stores, and store views from a single Magento installation.
