Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Definition:
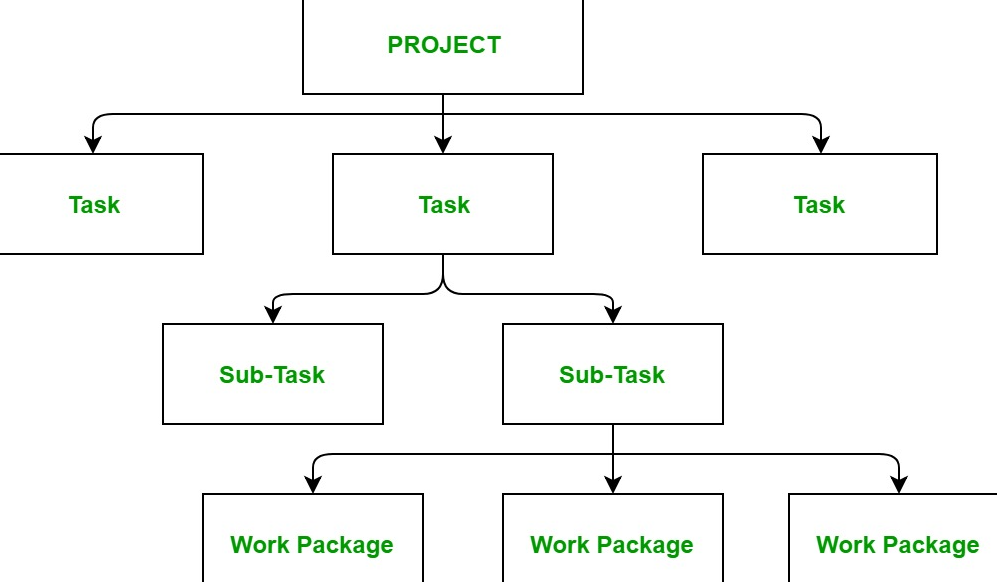
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of a project into smaller, manageable components. It breaks down the project scope into deliverables and tasks, making it easier to plan, execute, monitor, and control the project. Each level of the WBS provides increasing detail about the work required to achieve the project objectives.
Purpose of the WBS
- Scope Clarity: Clearly defines the project scope by outlining all deliverables and tasks.
- Manageability: Divides the project into manageable sections, making it easier to assign responsibilities and track progress.
- Baseline for Planning: Provides a framework for scheduling, budgeting, resource allocation, and risk management.
- Communication Tool: Enhances communication by presenting the project structure visually.
Structure of a WBS
The WBS is typically visualized in a tree-like diagram or outline format with multiple levels:
- Level 1: The Project Name or overall deliverable (e.g., “New Office Construction”).
- Level 2: Major deliverables or phases of the project (e.g., “Design,” “Construction,” “Move-In”).
- Level 3 and Beyond: Breaks down deliverables into smaller, detailed tasks (e.g., “Order Furniture,” “Install Wiring,” etc.).
Key Characteristics of a WBS
- Deliverable-Oriented: Focuses on outcomes rather than activities.
- 100% Rule: All work required for the project must be included in the WBS, ensuring nothing is missed.
- Mutually Exclusive: Each WBS element should be distinct to avoid overlap or redundancy.
- Hierarchical: The structure progresses from high-level deliverables to more detailed tasks.
Steps to Create a WBS
- Define the Project Scope: Understand the goals, deliverables, and requirements of the project.
- Identify Major Deliverables: Break the project into high-level components or phases.
- Decompose Deliverables: Divide each deliverable into smaller, more detailed components until manageable tasks are identified.
- Assign Unique Codes: Assign identifiers to each WBS element for tracking (e.g., 1.1, 1.2.1).
- Validate the WBS: Ensure all project work is accounted for and follows the 100% Rule.
Formats of WBS
- Tree Diagram: Visual hierarchical structure.
- Outline/Tabular Format: Indented list showing the hierarchy.
- Mind Map: Creative and visual representation of deliverables.
Example of a WBS
Project Name: Office Relocation
| Level 1: Project | Level 2: Major Deliverables | Level 3: Subtasks |
|---|---|---|
| Office Relocation | 1. Design | 1.1 Finalize Floor Plan |
| 1.2 Obtain Necessary Approvals | ||
| 2. Construction | 2.1 Demolish Existing Partitions | |
| 2.2 Install Wiring and Networking | ||
| 3. Move-In | 3.1 Pack Existing Office Materials | |
| 3.2 Transport and Set Up Equipment |
Benefits of WBS
- Improved Planning: Provides a clear roadmap for project execution.
- Better Resource Allocation: Helps allocate resources effectively by breaking down tasks.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Enables tracking of progress and performance against deliverables.
- Reduced Risks: Identifies potential risks by detailing all work elements.
WBS vs. Project Schedule
- WBS focuses on breaking down deliverables into tasks.
- Project Schedule focuses on the timing and sequencing of tasks.
Conclusion
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a foundational tool in project management. It ensures clarity, structure, and organization, allowing project teams to manage scope effectively and deliver results on time and within budget.
